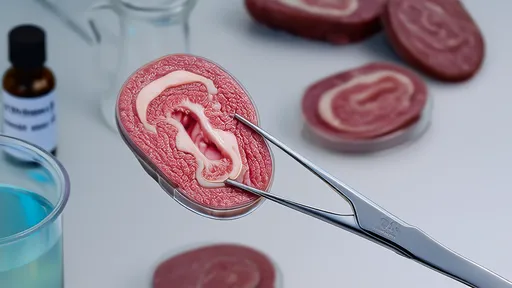
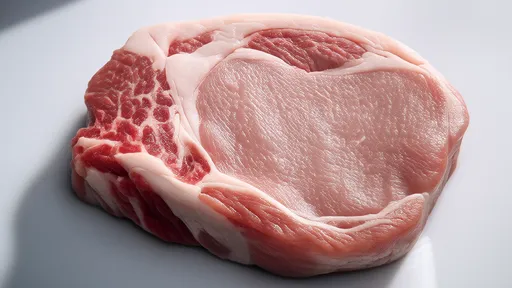
The marbling phenomenon in pork, often referred to as "snowflake pork," has captivated both culinary experts and meat scientists alike. This intricate pattern of intramuscular fat deposition not only enhances flavor and tenderness but also represents a fascinating interplay of genetics, nutrition, and animal physiology. Understanding the science behind this fat deposition reveals why certain cuts command premium prices in global markets.
At the cellular level, intramuscular fat develops when adipocytes (fat cells) accumulate within the perimysium connective tissue surrounding muscle fiber bundles. Unlike subcutaneous fat which forms visible layers beneath the skin, marbling fat infiltrates the muscle structure itself. The process begins during the animal's growth phase when precursor cells called preadipocytes differentiate into mature fat cells under specific hormonal and metabolic conditions.
Genetic predisposition plays a paramount role in determining an animal's capacity for marbling. Certain pig breeds, particularly those originating from Asian bloodlines like the Japanese Kurobuta or Chinese Meishan, possess genetic markers associated with enhanced intramuscular adipogenesis. These genetic factors influence the activity of enzymes like lipoprotein lipase which regulates triglyceride uptake into developing fat cells.
The nutritional program of pigs destined for high-quality pork production significantly impacts marbling development. During the finishing phase (typically the last 30-45 days before slaughter), specialized diets rich in unsaturated fatty acids and fermentable carbohydrates promote ideal fat deposition. The relationship between nutrition and marbling isn't linear - excessive energy intake can lead to undesirable subcutaneous fat rather than the prized intramuscular pattern.
Hormonal regulation provides another layer of complexity in marbling formation. Insulin sensitivity in muscle tissue, mediated by growth hormones and adipokines like leptin, determines how efficiently nutrients convert into intramuscular fat. Modern production systems sometimes utilize dietary supplements containing conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) or vitamin D3 to optimize these metabolic pathways without compromising animal welfare standards.
Environmental factors including stress management and housing conditions indirectly influence marbling quality. Chronic stress triggers cortisol release which can repress adipogenesis in muscle tissue. This explains why premium pork producers invest in low-stress handling systems and enriched environments that allow pigs to exhibit natural behaviors throughout the production cycle.
The timing of harvest represents a critical determinant of marbling quality. Unlike beef which continues developing intramuscular fat over extended periods, pork reaches optimal marbling at younger ages. Most high-quality pork programs harvest animals between 6-8 months when the balance between muscle development and fat deposition achieves perfect harmony. Advanced ultrasound technologies now allow producers to monitor marbling progression without invasive procedures.
Postmortem handling further refines the final marbling appearance. The interplay between pH decline during rigor mortis and fat distribution affects how prominently the marbling pattern appears to consumers. Rapid chilling techniques developed in recent years help preserve the delicate fat structure while meeting food safety requirements.
From a culinary perspective, the melting point of intramuscular fat differs significantly from other fat deposits. Rich in oleic acid (the same monounsaturated fat found in olive oil), marbling fat liquefies at lower temperatures, basting the muscle fibers from within during cooking. This explains the exceptional juiciness and flavor release characteristic of properly prepared snowflake pork.
Modern breeding techniques have made significant strides in balancing leanness with marbling quality. While traditional breeds naturally deposited more fat, contemporary genetic selection allows for precise marbling development without excessive backfat. Genome-wide association studies continue identifying new markers linked to favorable fat deposition patterns, enabling more efficient production of consistently marbled pork.
The global market for premium marbled pork continues expanding as consumers recognize its superior eating quality. Specialty producers now employ intricate grading systems similar to beef, evaluating marbling distribution, fineness, and overall muscle quality. This shift reflects growing appreciation for pork as a center-of-the-plate gourmet ingredient rather than merely a commodity protein source.
Research into alternative production methods has yielded interesting findings about marbling development. Some studies suggest that controlled exercise regimens can enhance intramuscular fat deposition by increasing metabolic demand within specific muscle groups. Others explore the impact of novel feed ingredients like spent brewery grains or olive byproducts on fat composition and oxidative stability.
Food scientists continue unraveling the complex relationship between marbling characteristics and sensory attributes. While fat quantity matters, the fatty acid profile and microscopic distribution patterns prove equally important in determining texture and flavor release. Advanced imaging techniques now allow researchers to map fat distribution at resolutions previously unimaginable.
As consumer preferences evolve toward more flavorful eating experiences, understanding intramuscular fat deposition becomes increasingly valuable. The snowflake pattern represents more than aesthetic appeal - it's a biological masterpiece resulting from careful genetic selection, precise nutrition management, and thoughtful production practices. This convergence of science and gastronomy ensures pork maintains its position as one of the world's most versatile and beloved proteins.

By /Jul 17, 2025

By /Jul 17, 2025
By /Jul 17, 2025

By /Jul 17, 2025
By /Jul 17, 2025

By /Jul 17, 2025
By /Jul 17, 2025

By /Jul 17, 2025

By /Jul 17, 2025

By /Jul 17, 2025

By /Jul 17, 2025

By /Jul 17, 2025

By /Jul 17, 2025
By /Jul 17, 2025

By /Jul 17, 2025

By /Jul 17, 2025
By /Jul 17, 2025
By /Jul 17, 2025

By /Jul 17, 2025
By /Jul 17, 2025